Ultrasonic-assisted bone instrument
Precise on bone, gentle on critical structures
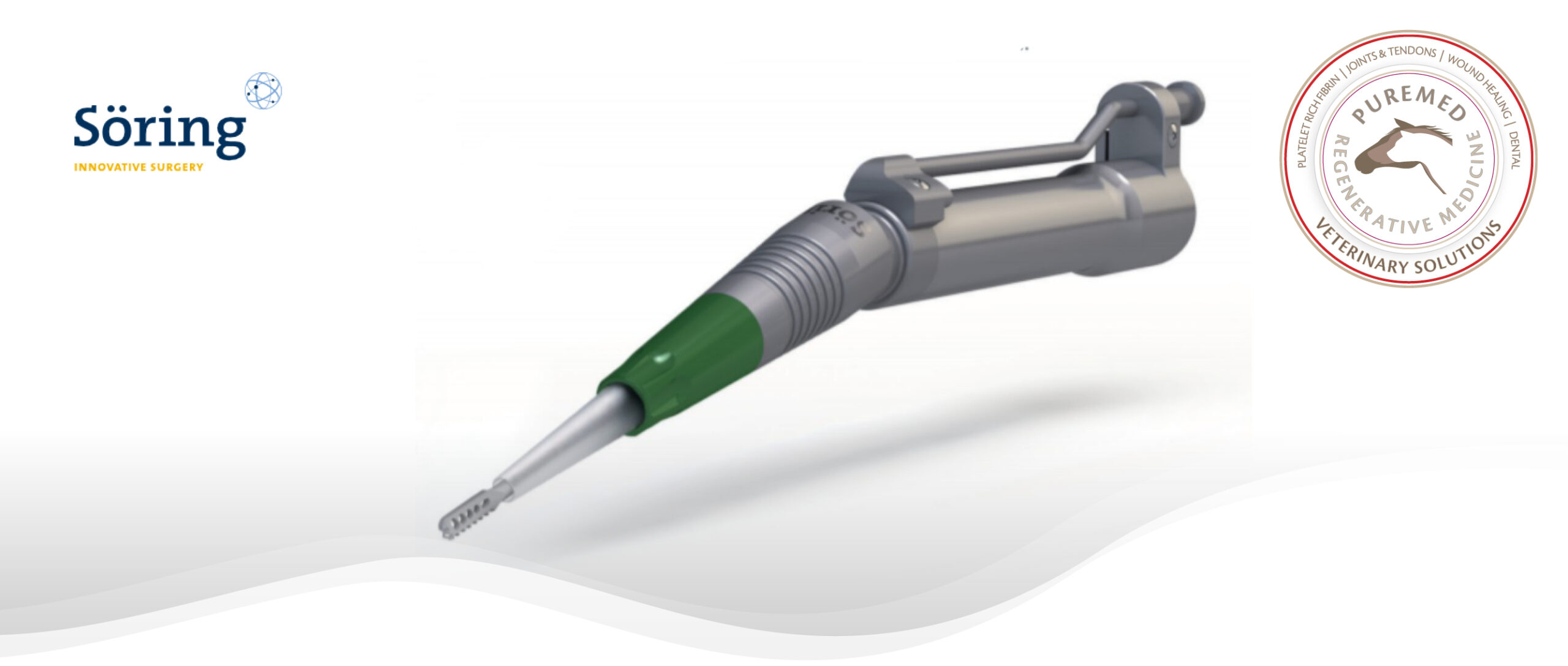
The ultrasonic-assisted bone instrument from Söring was explicitly developed for the resection of bone and offers numerous advantages in spinal surgery, e. g. for decompression procedures. The non-rotating technology allows an exact and delicate approach so that the surgeon can work closely with critical spinal neurovascular structures such as the dura mater. Additional pressure is avoided, which is extremely important when working in already tight spaces. Due to the longitudinal movement of the sonotrode tip, there is also no risk of “grabbing.”
Another great advantage compared to other instruments is that bone can be removed in individual pieces, as it is not ground. Thus, the removed material can be used further for fusion operations. Therefore, artificial bone material or bone graft harvesting can be avoided.
Different sonotrodes for an individual procedure
The surgeon can choose between two sonotrode shapes and lengths and optimize the instrument regarding indication, procedure, and access route.

Knife sonotrode
The blade-shaped sonotrode cuts out vital bone pieces precisely and with a straight-cut surface.
- Longitudinal ultrasonic oscillations (35,000 times per second)

Rasp sonotrode
The rasp-shaped sonotrode is used for precise bone ablation.
- Longitudinal ultrasonic oscillations (35,000 times per second) in combination with torsional motion
What is needed?
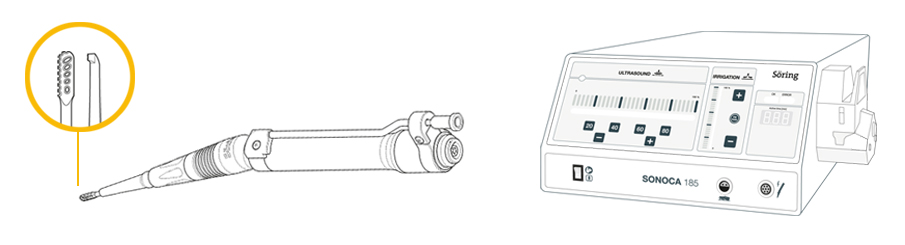
- single use sonotrode (rasp or knife)
- reusable bone instrument
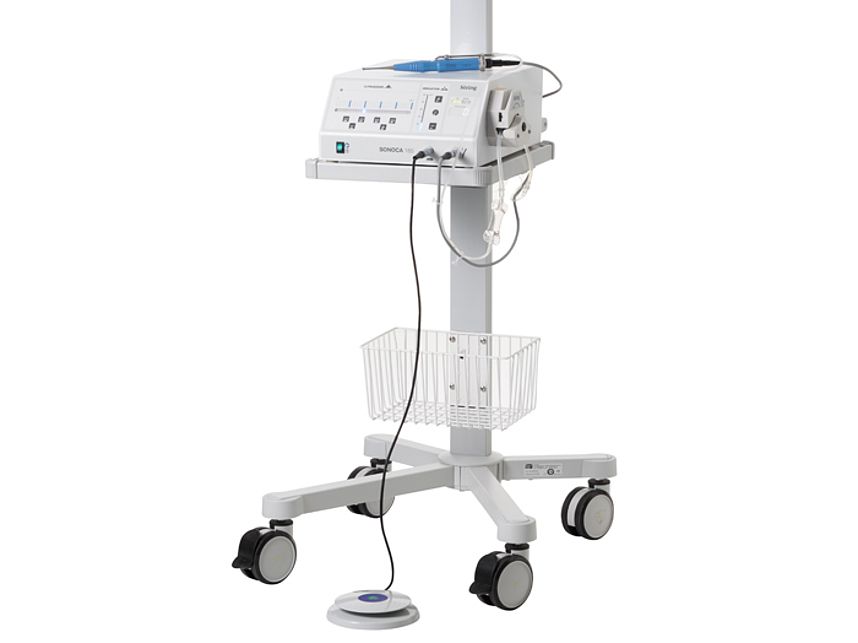
- ultrasonic generator SONOCA 185 or SONOCA 300 and accessories
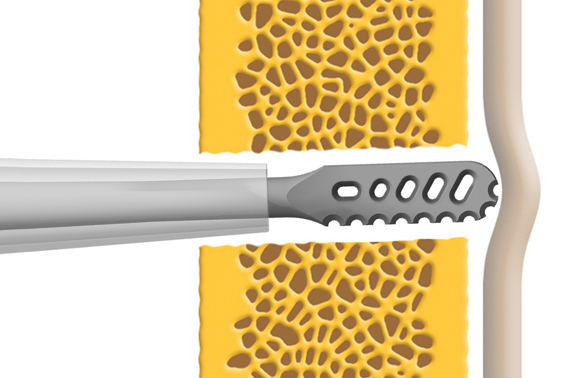
Principle of ultrasonic technology in spinal surgery
The ultrasonic oscillations of the sonotrode tip and the manual movement of the bone instrument allow precise and controlled cutting through bone and targeted bone removal. Elastic structures are significantly more resistant to ultrasonic oscillations. Since they can adapt to the oscillations, they remain intact in the event of contact with the sonotrode tip.
Click the button to see how Söring Wound Debridement works.
Click the button to see how Söring Hepaccs instruments facilitate Organ and Soft Tissue Surgery.